Common Pediatric Dental Procedures Every Parent Should Know
As a parent, ensuring your child’s health includes giving proper attention to their dental care. Pediatric dentistry plays a vital role in monitoring and maintaining your child’s oral development—from their first tooth to their teenage years. Understanding common pediatric dental procedures can help you feel more confident and proactive when visiting the dentist.
In this guide, we’ll break down the most frequent treatments offered by pediatric dentists, what to expect during each procedure, and why they’re important for your child’s overall health.
Why Pediatric Dentistry Matters
Children’s teeth are more than just placeholders for adult teeth. Early dental care helps prevent future problems, promotes healthy oral habits, and builds comfort around visiting the dentist.
Benefits of early pediatric dental care:
- Prevents tooth decay and cavities
- Encourages proper jaw and bite development
- Educates children on brushing and flossing
- Reduces dental anxiety over time
Most Common Pediatric Dental Procedures
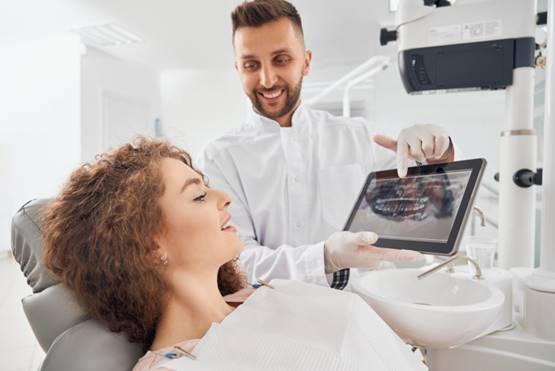
- Dental Examinations and Cleanings
These are the cornerstone of preventive care. Pediatric dentists recommend check-ups every six months.
What to expect:
- Visual inspection of teeth and gums
- Gentle cleaning to remove plaque and tartar
- Fluoride treatment to strengthen enamel
Why it matters: Helps detect early signs of cavities, gum disease, or misalignment.
- Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride is a natural mineral that strengthens tooth enamel and prevents decay.
When it’s done: Usually during routine check-ups
Process:
- Fluoride gel or varnish applied to teeth
- Takes just a few minutes
- No eating or drinking for 30 minutes afterward
Why it matters: Essential for cavity prevention, especially in children with early signs of enamel wear.
- Dental Sealants
Sealants are thin, protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth (molars).
Best age to apply: Ages 6 to 14, as soon as permanent molars erupt
Benefits:
- Prevents food and bacteria from settling in grooves
- Reduces cavity risk in molars by up to 80%
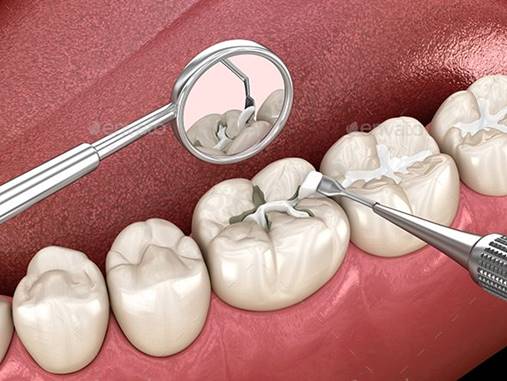
- Cavity Fillings
Despite best efforts, some children may still develop cavities that require fillings.
Materials used:
- Tooth-colored composite resin (most common)
- Amalgam (less common today)
Procedure:
- Area is numbed
- Decay is removed
- Filling is placed to restore the tooth’s shape and function
- Pulp Therapy (Baby Root Canal)
If a cavity reaches the nerve of a baby tooth, pulp therapy may be needed to save the tooth.
Types:
- Pulpotomy: Removal of the infected part of the pulp
- Pulpectomy: Full removal of pulp tissue, often followed by a crown
Why it’s important: Preserving baby teeth maintains spacing and guides proper eruption of permanent teeth.
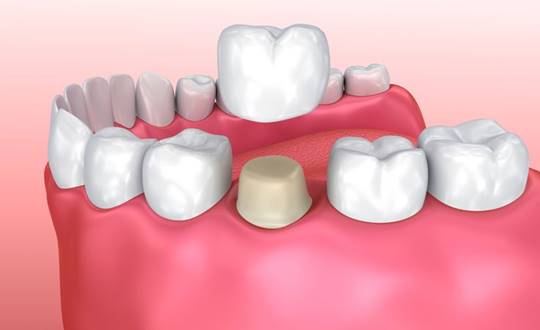
- Dental Crowns for Children
Used when a tooth is severely decayed or damaged, especially after pulp therapy.
Types:
- Stainless steel crowns (durable and cost-effective)
- Tooth-colored crowns (used for front teeth)
Purpose: Protects the tooth and restores function until it naturally falls out.
- Tooth Extractions
Sometimes a tooth needs to be removed due to severe decay, infection, or crowding.
Common reasons:
- Baby tooth that won’t fall out naturally
- Orthodontic preparation
- Infected or abscessed tooth
Your child’s comfort: Local anesthesia and gentle techniques make this safe and manageable.
- Space Maintainers
If a baby tooth is lost prematurely, a space maintainer may be needed to hold the gap open for the permanent tooth.
Why it’s done: Prevents neighboring teeth from shifting and blocking the erupting tooth.
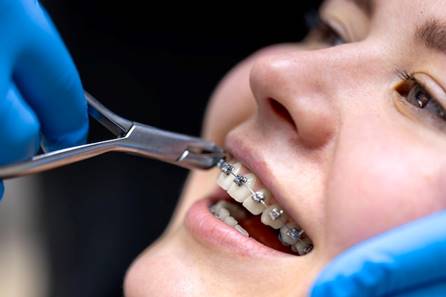
- Orthodontic Evaluations
Most pediatric dentists begin monitoring bite alignment and jaw development by age 7.
Early signs of concern:
- Crossbite or overbite
- Crowded or spaced teeth
- Thumb-sucking past age 4
Next steps: May refer to an orthodontist for early intervention or future braces.
Tips for Parents: Preparing Your Child for Dental Visits
- Talk positively about the dentist—avoid words like “pain” or “shot”
- Read dental-themed children’s books to set expectations
- Reward good behavior after the visit, not before
- Choose a pediatric dental office experienced in treating children with patience and care
Conclusion: Start Early, Stay Informed
Knowing what to expect during pediatric dental visits can help you support your child with confidence and ease. These common procedures—from routine cleanings to more advanced treatments—are designed with your child’s comfort, development, and long-term oral health in mind.